Python programm: estimating tree biomass using allometry
A Python program for estimating above-ground biomass at a single tree level using allometric equations
A python program was developed, which integrated a comprehensive set of allometric equations for above-ground biomass calculating at a single tree level.
The empirical allometric equations using DBH and H as predictors. There are totally 10 equations were integrated into the program, these are most frequently used equations in previous studies.
The program will fit provided tree data with one by one equation. For each equation, the equation itself and its parameters will be displayed, along with regression visualization, finally, accuracy assessments of MAE, MSE, RMSE, and R2 will be all shown. The users are asked to type Enter to continue seeing the results.
The equations were compiled from previous studies which research empirical equations for biomass estimating for different tree species in Europe. Therefore, the empirical equations are most appropriate for European tree data due to their own characteristics. The author of the program, hence, suggests users apply the program for European tree data for better results.
Getting started
💻 code of the program can be found on here
📚 Install required Python libraries using dependencies.txt
🤔 the program generates figures, an environment that supports visualization should be used.
Method
The main idea of the program is to use provided information of tree diameter (DBH), tree height (H), and tree biomass (AGB) apply into predefined equations to generate a set of equation parameters that best fit the data. From determined parameters, the biomass value will be predicted. The predicted biomass and the actual biomass then will be compared by visualization and accuracy assessment.
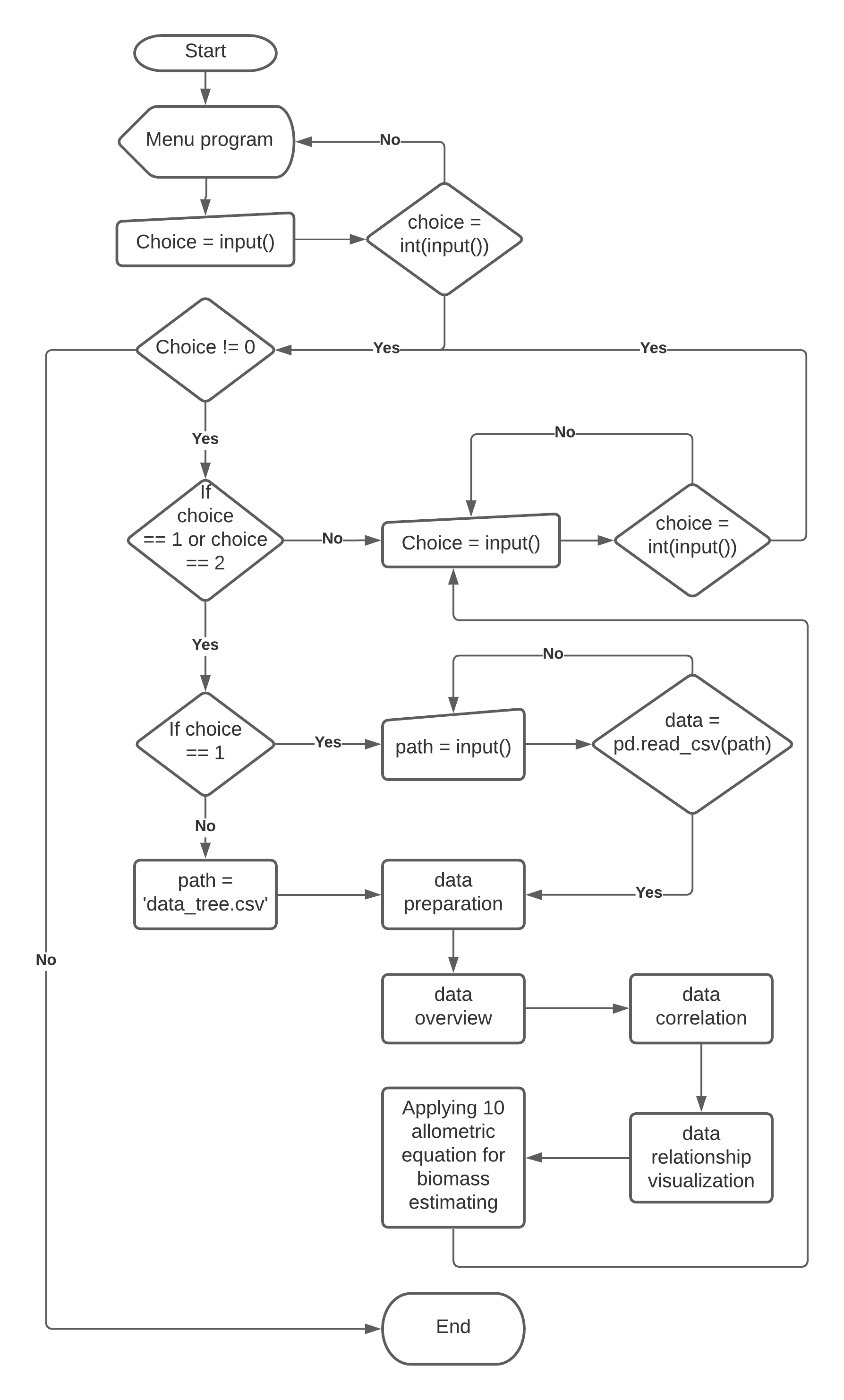
The main program is under a while loop which only will be executed in case the user input is 1 or 2. The two options of input according to two options the program offers the users, which are processing the user’s data file or built-in data file, respectively.
- With the input of 1, users asked for their file path.
- On the other hand, the file path is set as “data_tree.csv” in case input of 2.
There is also a chance to exit while loops (main program) with 0 input.
Data from users
There are some requirements that data from users have to be fulfilled:
- Data file in CSV format
- Decimals separated by dots
- Data contains at least three columns with exact names as DBH, H, AGB. Column DBH, H, AGB contain data from diameter at breast height, tree height and above-ground biomass, correspondingly.
- The units for the three columns DBH, H, AGB are centimeter (cm), meter (m) and kilogram (kg), respectively.
Built-in data
📁 The built-in data contains information of 90 Scots pine trees ranging around 20 - 100 years old in Poland.
Descriptive statistic
After defining data will be used, the next process so-called “descriptive statistic”. The section implemented various processes including data preparation, displaying overview statistics of the data and visualizing data relationships.
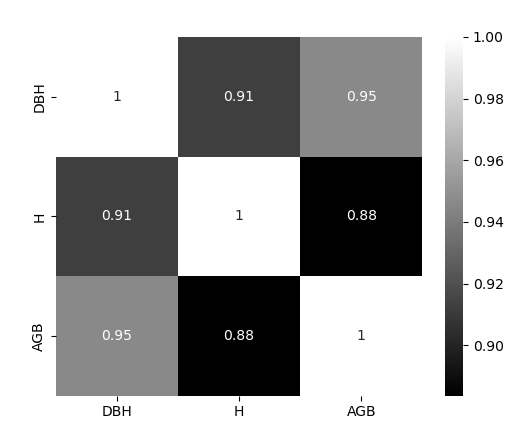
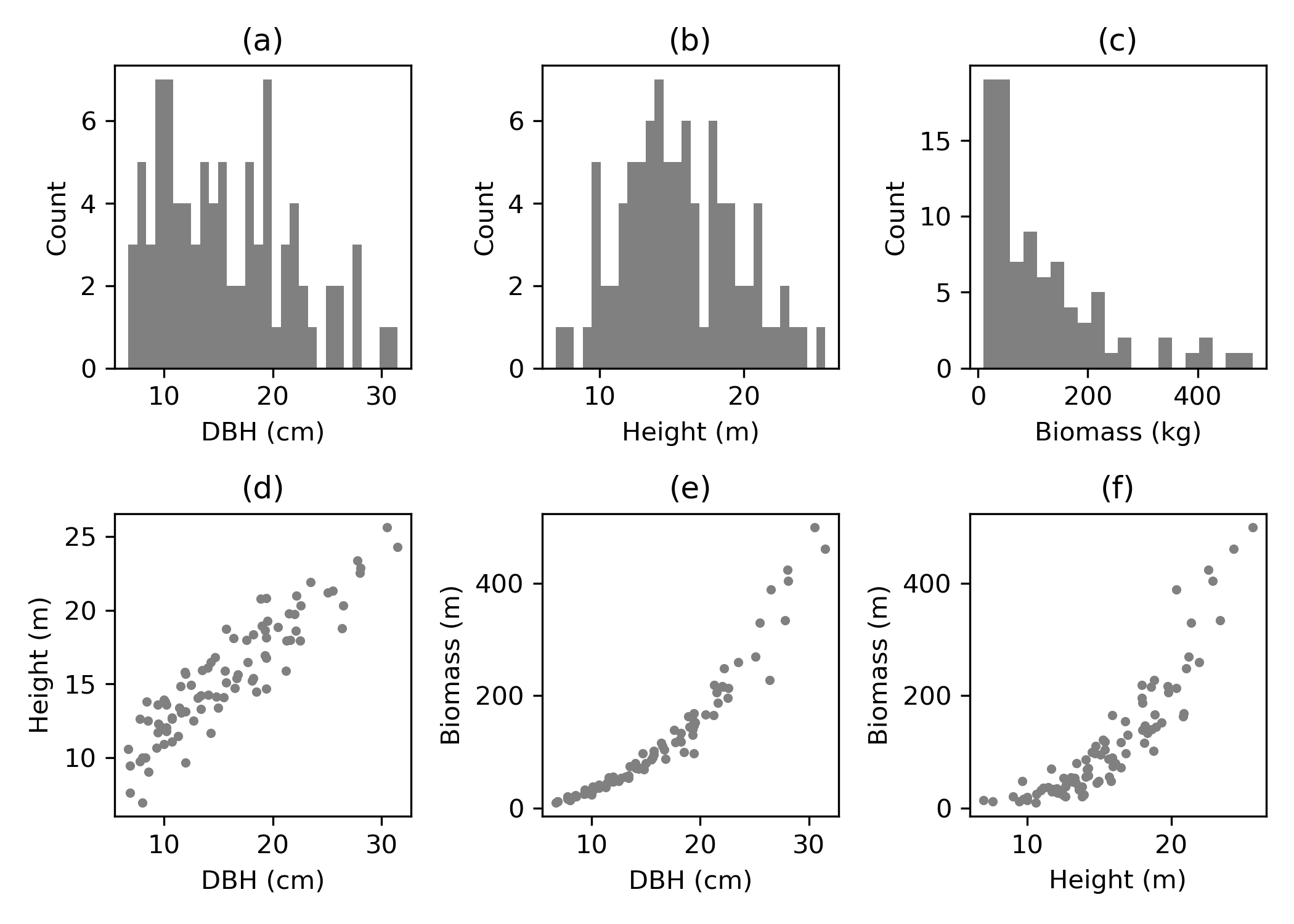
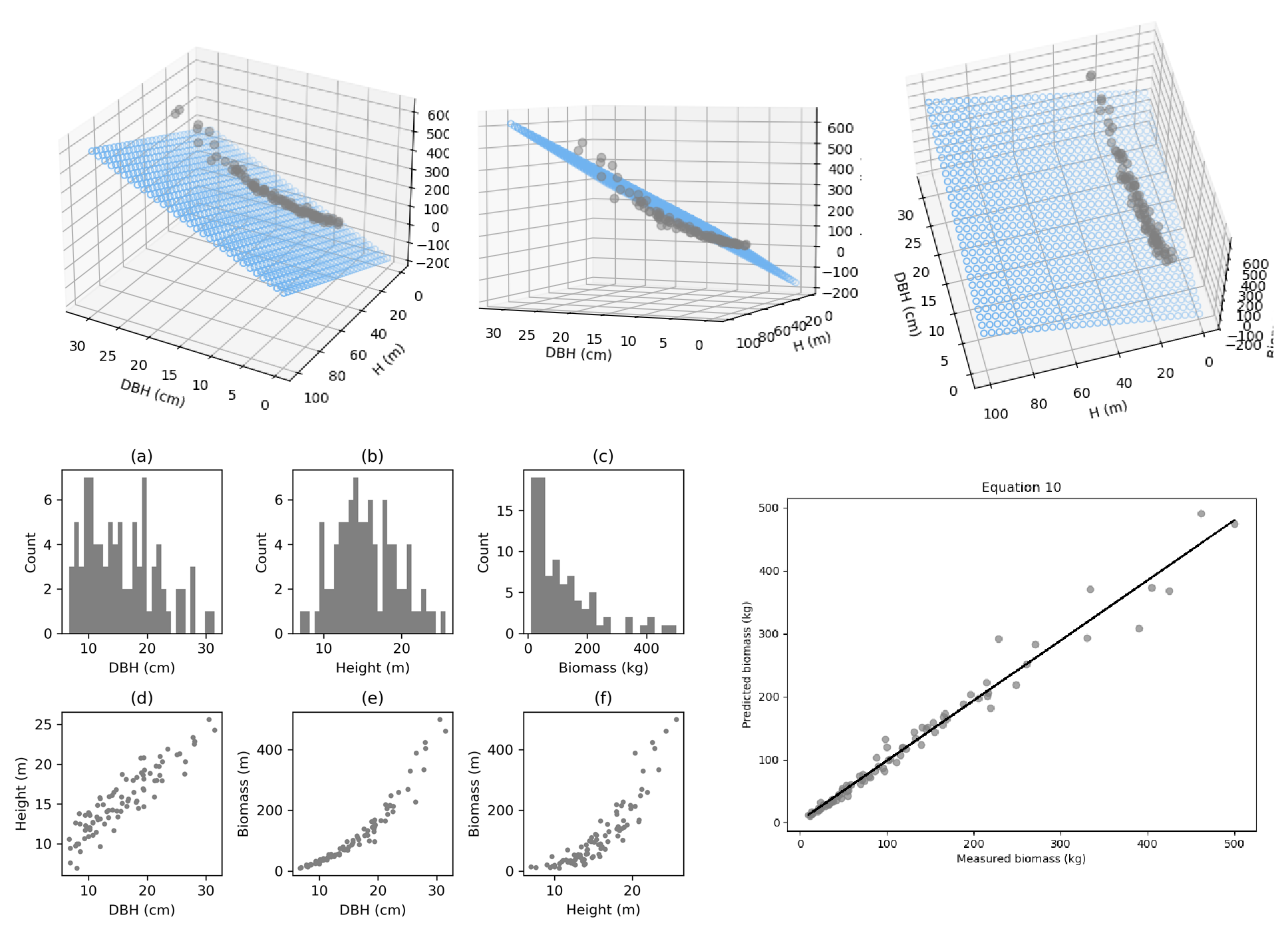
Allometric equation
Tree biomass will be estimated based on equations in previous studies, some of which consider exclusively diameter at breast height or tree height while others based on both parameters.
- W = a + b×DBH
- W = a + b×H
- W = a + b×DBH + c×H
- W = a + b×DBH^2
- W = a + b×DBH + c×DBH^2
- W = a + b×ln(DBH)
- W = a + b×log(DBH)
- W = a + b×DBH^2 + c×H^2
- W = a + b×log(DBH^2×H)
- W = a×DBH^b×H^c
Where: W- dry biomass, DBH - diameter at breast height, H - height, and a, b, c - model parameters.
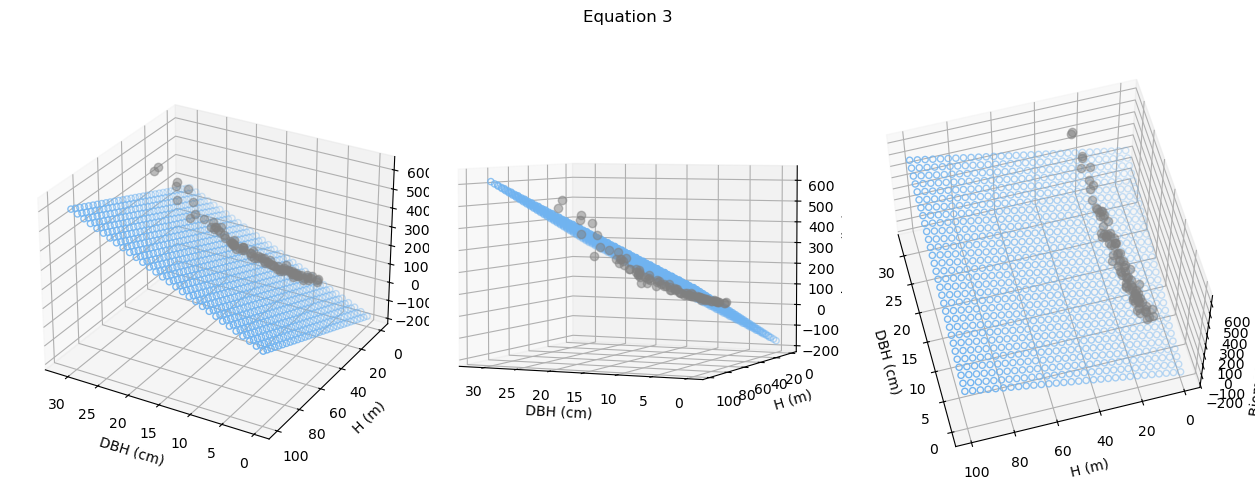
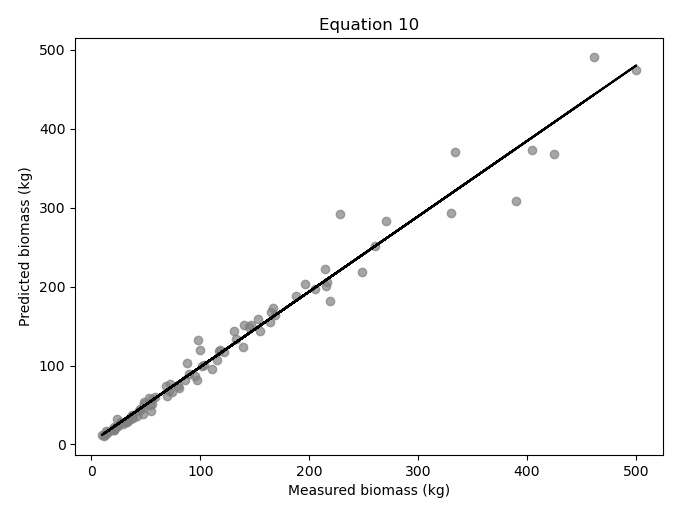
Accuracy
All models will be fit to data and the following goodness-of-fit measures will be provided for user’s assessment: coefficient of determination (R2), Mean Absolute Error (MAE), Mean Squared Error (MSE), and Root mean squared error (RMSE).